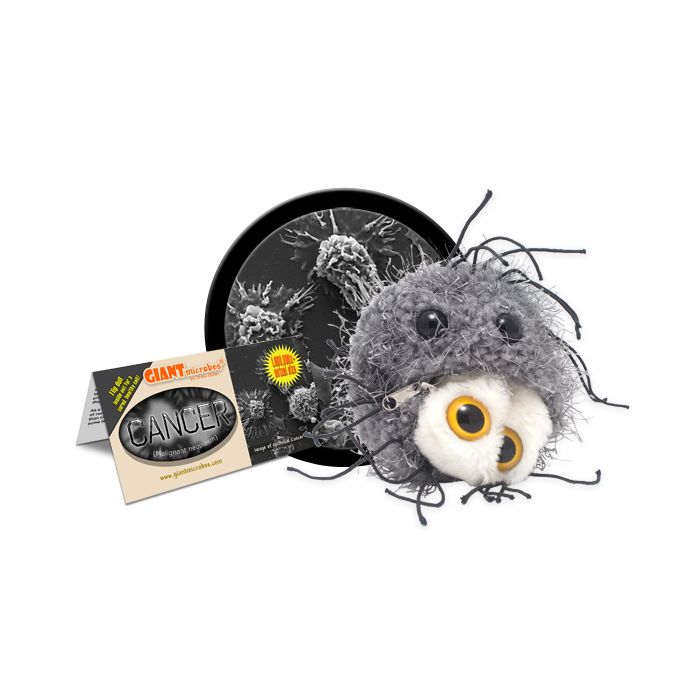
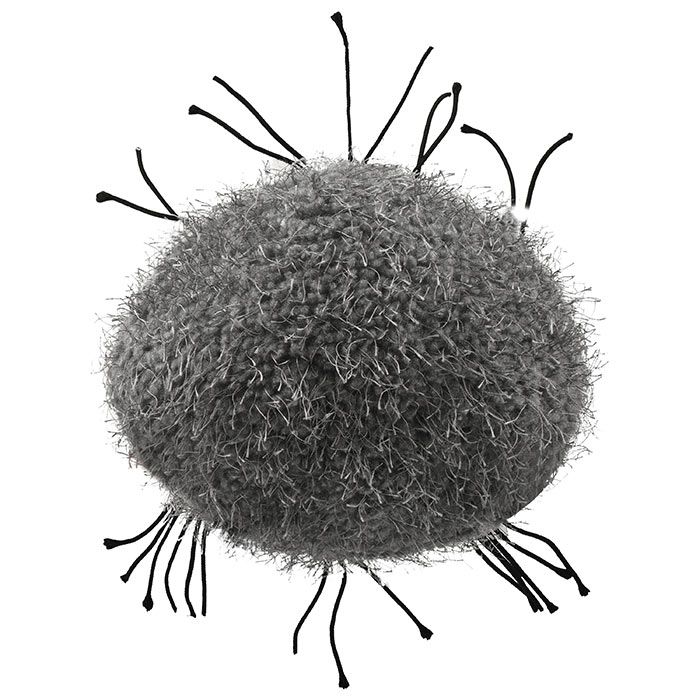
Cancer (Malignant neoplasm)
Our Cancer cell can be cured by turning it inside-out!
Product Details
Additional Information
| Sizes | Giantmicrobes are based on actual microbes, cells, organisms and other critters, only 1,000,000 times actual size! Gigantic (GG) 40-60cm XL (XL) 25-38cm Original (PD) 12-20cm Minis (MM) 5-10cm each Keychain (KC) 5-10cm with clip |
|---|---|
| Materials | Plush from all new materials. Stuffed with polyester fiber fill. Surface washable: sponge with water & soap, air dry. |
| Packaging | Each plush microbe includes a printed card with fun, educational and fascinating facts about the actual microbe or cell. |
| Safety | Every product meets or exceeds U.S. and European standards for safety. For ages 3 and up. |
All about Cancer (Malignant neoplasm)
FACTS: Few words awaken our most atavistic fears as strongly as the word "Cancer." But the word has quite a humble origin: the Greek physician Hippocrates (460-370 BC) was reminded of a crab when he saw the spreading tendrils of a tumor – and he named the disease "karkinos," or crab, later Latinized to "cancer."
The name "cancer" now applies to a group of more than 100 different diseases, all of which have two things in common. As a result of genetic damage, normal cells become cancerous and can grow in an uncontrolled manner. In addition, these cells are able to invade other tissues, disrupting and destroying the structures and organs that they infiltrate. (Without this second ability, tumors can only grow in a limited way, and are termed "benign.")
Why do cancers develop? Genetic inheritance certainly plays a role. But there are many other risk factors including smoking, excessive alcohol consumption or sun exposure, poor diet, and inadequate exercise.
Although the fundamentals of cancer treatment – surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy – have not changed in many years, advances in imaging of tumors, together with more sophisticated methods for delivering therapies, have greatly improved their effectiveness. In addition, new "biologic" and targeted therapies have also been developed that act directly on the cellular processes that cause cancer cells to behave so destructively. Finally, early diagnosis identifies cancers before they have a chance to spread.
As a result, many people who develop cancer have a greatly improved chance of recovery than was the case even just a few years ago. In fact, while more than one-third of women and almost half of all men will develop cancer at some time in their life, most will survive the experience.
| Name | The name was given by the Father of Medicine, Hippocrates, and originates from the Greek word “carcinos”, which describes tumors. |
|---|
| Where It Lives | Our bodies are made of billions of cells that are programmed to grow, divide, and die over time. When any cells don’t die, it can cause cancer. Cancer is a group of genetic disease caused by uncontrolled division of abnormal cells in the body. It can be inherited from our parents or result from DNA damage during a person’s lifetime. The type of cancer depends on where it’s located and type of DNA damage done. There are over 100 forms of cancer! |
|---|
| Symptoms | Symptoms of cancer depends on where in the body it’s located. Most cancers, such as breast and lung cancers, form tumors. Leukemia, or cancer of the blood, circulate around the body and don’t form tumors. The tumors can be benign or malignant. A benign tumor isn’t cancerous and doesn’t cause damage to the cells around them, but malignant tumors will destroy the surrounding normal cells and damage healthy tissues. Some grow fast and some grow slow. |
|---|
| Cure | Treatment varies with each individual, but most people undergo a combination of treatments, such as surgery with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy. |
|---|
| History | The first documented description of cancer was written by Edwin Smith Papyrus around 3000 B.C. |
|---|
| Fascinating Facts |
Tobacco use is the single largest preventable cause of cancer in the world! Over 30% of cancers can be prevented by not using tobacco, maintaining a healthy diet, being physically active, and limiting alcohol consumption. Famous people who died of it: 2005: Peter Jennings, a beloved TV reporter and heavy smoker, died of lung cancer. 2011: Steve Jobs, the founder of Apple computers and creator of the iPhone, died of pancreatic cancer after battling it for 7 years. |
|---|