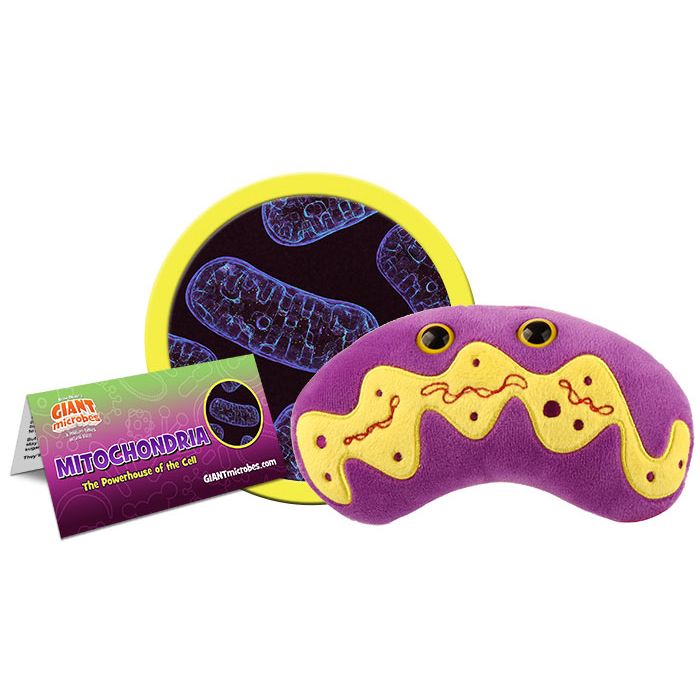
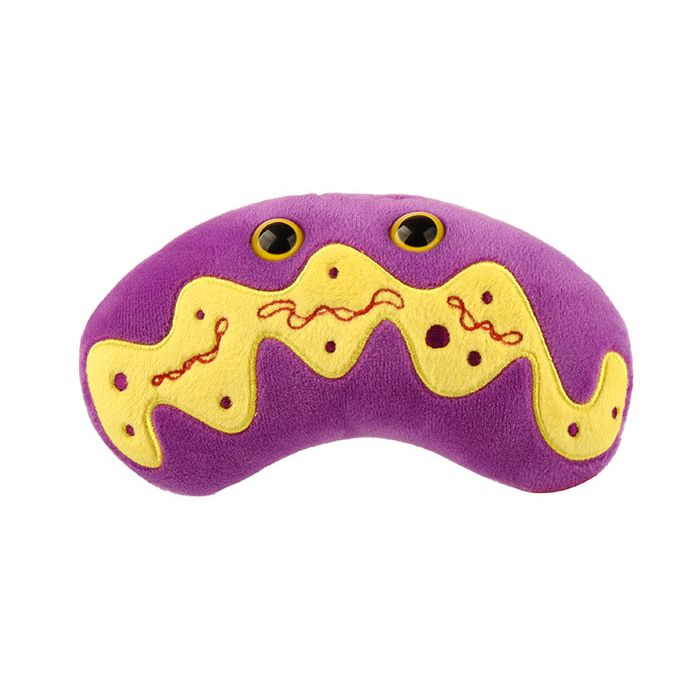
Mitochondria
Out of Stock
Meet the powerhouse of the cell - in plush form! This vibrant and scientifically accurate Mitochondria plush is inspired by the real organelle found in animal, plant, fungal, and other eukaryotic cells. It’s the perfect educational gift for biology students, science teachers, and anyone fascinated by cell biology.
Mitochondria are responsible for producing ATP, the engine behind cellular activity, by converting oxygen and nutrients into fuel. Now you can bring that cellular energy to your classroom, lab, or home with this adorable and informative plush toy. Includes a printed card packed with fun facts and educational details about mitochondria and their essential role in cellular respiration.
Product Details
Additional Information
| Sizes | Giantmicrobes are based on actual microbes, cells, organisms and other critters, only 1,000,000 times actual size! Gigantic (GG) 40-60cm XL (XL) 25-38cm Original (PD) 12-20cm Keychain (KC) 5-10cm with clip |
|---|---|
| Materials | Plush from all new materials. Stuffed with polyester fiber fill. Surface washable: sponge with water & soap, air dry. |
| Packaging | Each plush microbe includes a printed card with fun, educational and fascinating facts about the actual microbe or cell. |
| Safety | Every product meets or exceeds U.S. and European standards for safety. For ages 3 and up. |
All about Mitochondria
FACTS: Mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, combine oxygen with food to generate energy for cells to move, divide and live. These organelles power the cells in animals, plants, fungi and other eukaryotic lifeforms. Mitochondria can be spherical, ovoid, branching, and even shape-changing! Some cells have only one mitochondria, but most have many. Cells with a lot of metabolic activity, such as liver cells, can have thousands.
Mitochondria have smooth outer membranes and folded inner membranes with tubular projections called cristae. They are filled with water and protein. Mitochondria also contain DNA and ribosomes packed with RNA. Mitochondrial DNA, or mtDNA, accounts for a tiny portion of our body’s total DNA, but it is notably distinct from DNA in the nucleus. Unlike nuclear DNA, which comes from both parents, mitochondrial DNA is passed to you from your mother only. Since this unique part of your genome comes from her egg cell, it can be used to establish maternal family ties.
Mitochondria are wonderful, yet most organisms do not have any at all. Living things are divided into eukaryotes and prokaryotes, with the exception of viruses. Eukaryotes – animals, plants, fungi and protists – have cells with mitochondria as well as nuclei with DNA. Prokaryotes – bacteria and archaea – are single-celled microbes without mitochondria nor other organelles aside from ribosomes. When life began 3.5 billion years ago, prokaryotes ruled our planet. After another 1.5 billion years or so, life got complicated and diverse.
One remarkable theory, called endosymbiosis, holds that the first eukaryotes engulfed smaller, free-living prokaryotic cells, which then became mitochondria and other organelles inside of more complex cells. These microbes established a mutually beneficial relationship and headed down the evolutionary path to become amoebas, waterbears, lizards, birds and human beings. So thanks mitochondria - thank you for the power to make us who we are today!