Malaria (Plasmodium falciparum)
Out of Stock
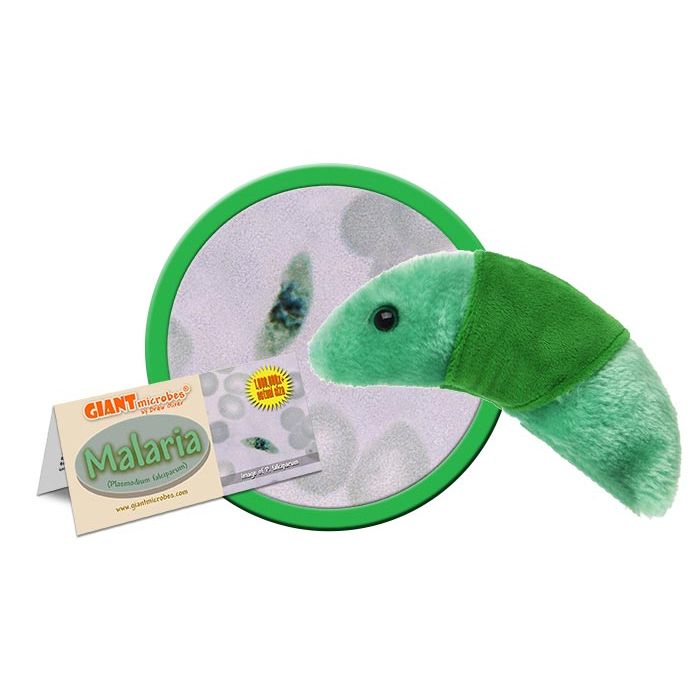
This plush representation of Malaria provides a memorable hands-on-way to learn about this global disease and how it is transmitted from the Anopheles mosquito. Unique, learning tool and gift for friends, family, public health experts, students, doctors, teachers and world travelers.
Soft, cuddly and memorable get well gift for recovering friends and loved ones. Great reminder to wear bug spray and prepare for the outdoors.
Features high quality materials, realistic design and comes with an educational card with fascinating facts about Malaria. Pairs well with our West Nile Virus plush.
Size: 5 x 3 x 3”

Your purchase supports Nothing But Nets, the world’s largest grassroots campaign to save lives by preventing malaria. It delivers millions of bed nets and other interventions to families in need. 10% of your purchase will be donated to Nothing But Nets.
Product Details
Additional Information
| Sizes | Giantmicrobes are based on actual microbes, cells, organisms and other critters, only 1,000,000 times actual size! Gigantic (GG) 16-24" XL (XL) 10-15" Original (PD) 5-8" Keychain (KC) 2-4" with clip |
|---|---|
| Materials | Plush from all new materials. Stuffed with polyester fiber fill. Surface washable: sponge with water & soap, air dry. |
| Packaging | Each plush microbe includes a printed card with fun, educational and fascinating facts about the actual microbe or cell. |
| Safety | Every product meets or exceeds U.S. and European standards for safety. For ages 3 and up. |
All about Malaria (Plasmodium falciparum)
FACTS: Malaria (Italian for "bad air") is the work of the Plasmodium parasite and the Anopheles mosquito. When the mosquito stings an infected person, parasites are absorbed as it draws up blood. As the mosquito continues her rounds (only the females are bloodsuckers), the parasites are distributed and the disease spreads. The liver is the initial locus of infection, but as red blood cells are subsequently attacked and compromised, they explode releasing the toxins that cause the fever and chills typical of the disease.
Once found throughout the tropics and subtropics, malaria has been all but eradicated from the developed world. (Early control efforts were instrumental in facilitating the completion of the Panama Canal.) In addition, tropical travelers can take anti-malarial drugs, use insect repellent (particularly at dawn and dusk when mosquitoes feed), wear long clothing, and sleep under nets or in protected housing.
However, for nearly 40% of the world's population, even these basic precautions can be unaffordable or impractical. As a result, up to half a billion people a year worldwide develop malaria, with more than a million fatalities, mostly African children.
Past eradication efforts have been doomed by resistance (both biological and political) to some of the insecticides and drugs used to combat Anopheles and Plasmodium. New efforts are now underway, and every 30 seconds counts...
| Name | Malaria comes from the Italian: Mala aria = bad air. People thought the disease came from the foul smelling air in some areas. |
|---|
| Where It Lives | Mosquitos carry the parasite and infect humans. It is not contagious. |
|---|
| Symptoms | The parasite infects red blood cells. Symptoms can range from fever, chills, sweats, and aches all the way to death. Severe malaria can have serious damaging effects on the red blood cells and organs. |
|---|
| Cure | Malaria can be treated with timely diagnosis and antimalarial drugs. However, it is becoming more resistant to standard antimalarial drugs. |
|---|
| History |
1880: Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran won a Nobel Prize for discovering the malaria parasites in a patient. 1897: Ronald Ross realized the role of mosquitos in carrying and spreading malaria. He won a Nobel Prize for his work. Big Outbreaks: Malaria was a problem in the U.S. until 1950, when the government worked to rid the country of the disease. Yearly cases decreased to 2000. |
|---|
| Fascinating Facts |
• Hundreds of millions of people get malaria each year, and over a million die. • It is most common in sub-Saharan Africa. • Less than 2000 people get malaria every year in the U.S., and those people have almost exclusively been travelers. • President JFK caught the malaria parasite during WWII. |
|---|