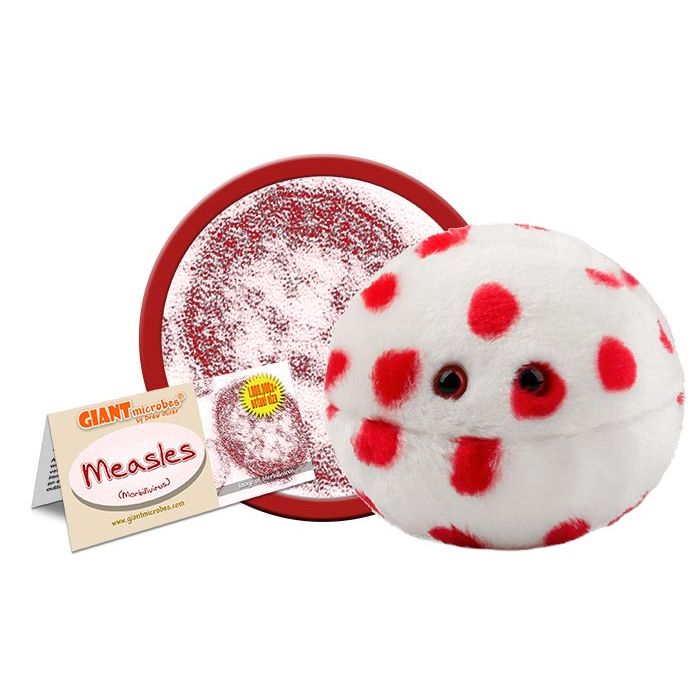
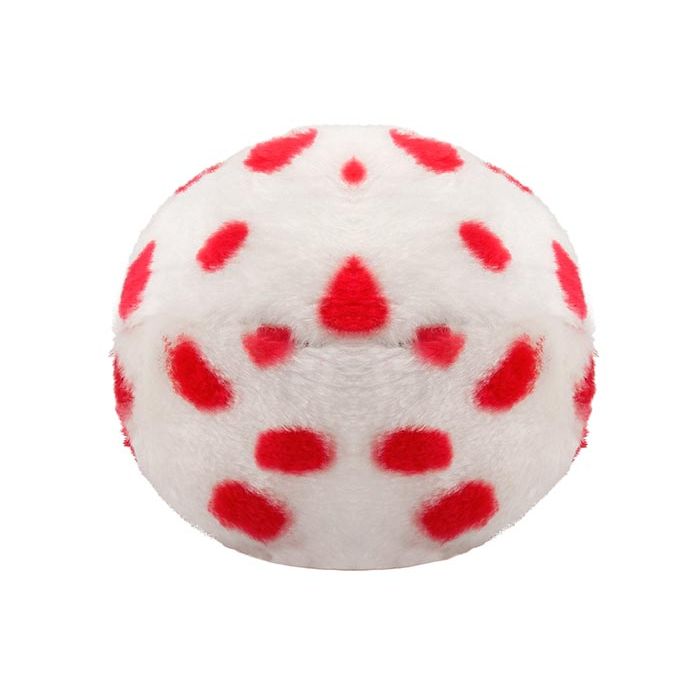
Measles (Morbillivirus)
Millions of people get Measles every year, despite a vaccine that's spot-on. Spread awareness with this adorable plush measles virus. GIANTmicrobes Measles provides a fun, hands-on-way to learn all about this disease, how it impacts your health and how to prevent it with the vaccine.
Cuddly and memorable, Measles is a unique biological gift for friends, family, students and teachers. A fun way to learn about microbes and vaccines, and an educational tool for doctors, nurses, scientists, public health experts and anyone with a healthy sense of humor. Includes an educational card with fascinating facts about the Measles.
Size: 6 x 5 x 5”
Product Details
Additional Information
| Sizes | Giantmicrobes are based on actual microbes, cells, organisms and other critters, only 1,000,000 times actual size! Gigantic (GG) 16-24" XL (XL) 10-15" Original (PD) 5-8" Keychain (KC) 2-4" with clip |
|---|---|
| Materials | Plush from all new materials. Stuffed with polyester fiber fill. Surface washable: sponge with water & soap, air dry. |
| Packaging | Each plush microbe includes a printed card with fun, educational and fascinating facts about the actual microbe or cell. |
| Safety | Every product meets or exceeds U.S. and European standards for safety. For ages 3 and up. |
All about Measles (Morbillivirus)
FACTS: Measles, sometimes known as rubeola, is a well-known, highly contagious virus. Although its telltale symptoms are body-covering red spots often accompanied by a mild fever, it is in fact a respiratory disease that can lead to life-threatening conditions such as pneumonia and encephalitis (or brain swelling and degeneration). And indeed, in countries where malnutrition and poor health are prevalent, measles infections can be fatal.
The good news is that in 1963 scientists synthesized a vaccine from a live rubeola virus, and nearly all children in the developed world are now inoculated against measles, typically along with mumps and rubella when they receive their MMR shot. (A vaccine against varicella, the virus which causes chickenpox, is now often included in the shot, making it the MMRV.)
However, in developing nations that lack widespread vaccination programs, measles remains a significant health threat. Indeed, the World Health Organization calls measles one of the leading causes of vaccine-preventable childhood death.
Fortunately, international efforts to vaccinate against measles are having a significant impact upon the incidence of measles worldwide. As global vaccination campaigns continue, additional lives will be saved.
(Measles is nicht to be confused with German measles vich is caused by a completely different wirus.)
| Name | Rubeola |
|---|
| Actual Size | 5.12 microns |
|---|
| Where It Lives | Measles live in the nose and throat mucus of an infected person. Measles virus can live for up to two hours in an airspace where the infected person coughed or sneezed! |
|---|
| System | The virus can spread if the eyes, nose, or mouth comes in direct contact with contaminated air or an infected surface. |
|---|
| Cure | A measles vaccine is available. This vaccine is so effective that measles is no longer constantly present in the United States! |
|---|
| Deadliness/Severity | Before the measles vaccination program, 3 to 4 million people got measles each year in the United States, killing 400 to 500 people and hospitalizing 48,000 people. Nowadays measles is quite uncommon, since many have the measles vaccine. |
|---|
| Infectiousness | Measles is so contagious that if one person has it, 90% of the people close to that person who are not immune will also become infected. |
|---|
| History |
One of the first written accounts of measles was published by a Persian doctor in the 9th century. In 1912 measles became a disease required by law to be reported to government authorities in the United States. In 1963 a measles vaccine was created and licensed in the United States. In 1968 this measles vaccine was improved and named “the Edmonston-Enders strain” because of its use of the Edmonston-B strain of measles virus. This vaccine has been the only measles vaccine used in the United States since 1968. |
|---|
| Fascinating Facts | Some people believed that the measles vaccine caused autism because of a 1998 study! |
|---|